Home › Forums › Let’s Talk Environment › The ABC of Climate Change
Tagged: climate, climate change, global warming, weather
- This topic has 0 replies, 1 voice, and was last updated 3 years, 8 months ago by
Hart.
-
AuthorPosts
-
-
01/07/2022 at 9:00 am #20431
Hart
KeymasterClimate change is an important topic globally because it impacts human lives.
It threatens the essential ingredients of good health – clean air, safe drinking water, nutritious food supply, and safe shelter – and has the potential to undermine decades of progress in global health.Join us on “LETS TALK ENVIRONMENT” as we discuss Climate Change.
Areas of Focus
- What is Climate Change?
- Is there a difference between Climate Change and Global Warming?
- What are the Causes of Climate Change?
- What are Greenhouse Gases?
- What are the sectors that contribute majorly to Global Warming?
- What are the Effects of Climate Change?
- What are the Social, Economic, and Environmental Impact of Climate Change?
- What are the global efforts put in place to combat Climate Change?
- What is the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement?
- What is the Net-Zero Transition?
- What are the Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies used to solve the problem of Climate Change?
What is Climate Change?
To understand the meaning of climate change, it is first necessary to understand the concepts of “weather” and “climate”.
Weather is the present or day-day atmospheric condition of a place. These conditions relate to temperature, humidity, precipitation, and wind. Weather is described in the present or short term. For example, the temperature in Uyo is 27°C today. This example tells you the weather condition in Uyo.
Climate is the average weather condition of a place over a long period, usually 30 years. Tropical regions are known to be hot and humid. Temperate regions are known to have low temperatures. And deserts are classified as arid because they are known to have low rainfall.
Climate Change is therefore the overall change in the average weather pattern of the earth’s surface over a long period. Changes in average temperature and precipitation (rainfall and snow) are all attributed to climate change.
Is there a difference between Climate Change and Global Warming?
Global Warming and Climate Change are used by most people interchangeably but there is a thin line between the two phenomena. Global warming is concerned specifically with the rise in temperature of the earth’s surface while climate change is a more complex phenomenon that encompasses changes in all weather and atmospheric conditions like temperature, precipitation (rainfall) and wind. Changes in frequency/intensity of precipitation and changes in wind speed are all related to climate change.
Global Warming is specifically an increase in the earth’s average temperature caused by greenhouse gases.
Climate Change is much more complex and entails changes in average temperature, precipitation and win patterns.
What are the Causes of Climate Change?
Climate Change is caused by a wide range of factors, some of the major causes will be discussed here today.
- Industrialization: production, and urbanization activities have led to an increase in the number of greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere. For example, the refrigeration industry has led to the emission of Fluorinated gases which are very potent greenhouse gases.
- Combustion Activities: activities that lead to the burning of fossil fuels, like oil and gas exploration, power generation, transportation, and other combustion activities contribute to the release of certain greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide.
- Deforestation: Cutting down trees for whatever purpose releases the carbon stored in them into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide. Furthermore, since trees act as carbon sinks, cutting them down without replacing them distorts the balance of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Agricultural Activities: agricultural activities like poultry production or livestock rearing result in the emission of greenhouse gases, particularly methane (CH4) and Nitrous oxide (N20). These gases contribute to climate change.
What are Greenhouse Gases?
Greenhouse gases are naturally occurring or man-made gases that trap heat from the sun on the earth’s surface.
Some common greenhouse gases are:
- Carbon dioxide
- Nitrous oxide
- Fluorinated gases
- Methane
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
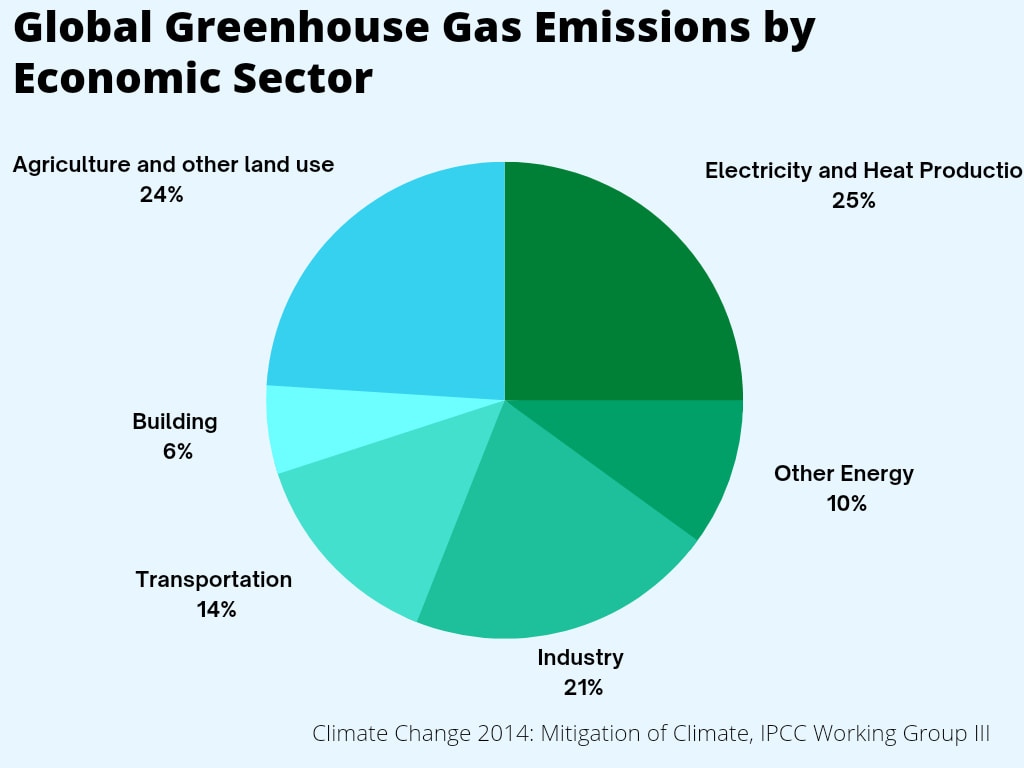
Sources of the greenhouse gases
- Carbon dioxide: is the most common type of greenhouse gas, it is emitted primarily from the combustion of fossil fuels, it is also released by certain man-made activities like deforestation, soil degradation, and agriculture.
- Methane: methane is released when waste is decomposed with little or no oxygen, agricultural activities and waste management are also activities that can lead to the release of methane into the atmosphere.
- Nitrous oxide: the use of fertilizer and the combustion of fossils are primary causes of nitrous oxide in the atmosphere.
- Fluorinated gases (chlorofluorocarbon, hydrofluorocarbons, Bromo fluorocarbons, hydrochlorofluorocarbons): these gases are contained in most consumer products like refrigerators, air conditioners, and foams. Emissions are usually during manufacturing or during the product life.
- Ozone: this gas is formed naturally in the atmosphere when heat from the sun causes a chemical reaction between certain hydrocarbons and nitrous oxide.
What are the sectors that contribute majorly to Global Warming?

What are the Effects of Climate Change?
Climate Change has various adverse effects. Some of them are Rising temperatures, rising sea levels, droughts, clean water shortages, unpredictable weather patterns, increase in extreme weather events, shifting precipitation patterns, ocean acidification land degradation, loss of wildlife, and biodiversity.
In 2019, the National Emergency Management Agency revealed floods had displaced approximately 1.9 million Nigerians. This was as a result of a shift in weather conditions due to climate change.
What are the Social, Economic, and Environmental Impact of Climate Change?
Climate Change has social, economic, and environmental impacts and they are all intertwined.
Some social impacts are displaced people, poverty, loss of livelihood, hunger, increased risk of diseases, and imbalance in food systems.
An example of this is the Lake Chad which diminished by 90%. Millions of people across the region were displaced and children suffered from malnutrition.
Economic impact of climate change is Gross Domestic Product (GDP) loss and the Economic Intelligence Unit has projected the GDP loss in the continents of the world by 2050.
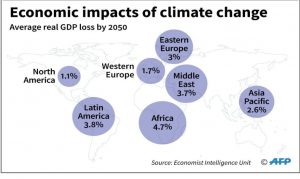
The continent of Africa has the highest percentage of GDP loss to climate change. There is therefore an urgent need to tackle climate change in Africa so as to reduce GDP loss by 2050.
Some environmental impacts are described by the World Metrological Center (WMO) and they are decrease in oxygen levels, ocean acidification, threat to ecosystems, coral bleaching, loss of mangroves and salt marshes.

What are the global efforts put in place to combat Climate Change?
Countries worldwide are striving to reduce carbon pollution and other greenhouse gas emissions and also adapt to the consequences associated with the rise in temperatures. There have been international climate change initiatives from the Rio Summit in 1992 to the Universal Paris agreement in 2015 and other annual COPs (Conference of Parties). Different countries have come up with mitigation and adaptation measures.
The UN Secretary-General has proposed six climate positive actions for governments to take once they go about building back their economies and societies:
- Green transition: Investments must accelerate the decarbonization of all aspects of the economy.
- Green jobs and sustainable and inclusive growth
- Green economy: making societies and people more resilient through a transition that is fair to all and leaves no one behind.
- Invest in sustainable solutions: fossil fuel subsidies must end and polluters must pay for their pollution.
- Confront all climate risks
- Cooperation/collaboration – no country can succeed alone.
Countries like Nepal, Bangladesh, and Burkina Faso have drawn up a climate strategy and action plan with a focus on agriculture. Small-scale farmers are assisted by incorporating climate-resilient agricultural practices, improving access to climate information, and building capacity.
What is the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement?
The Paris Agreement is a legally binding international treaty on climate change. It was adopted by 196 Parties at COP 21 on the 12th of December 2015 and entered into force on 4 November 2016. Its goal is to limit global warming to well below 2, preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius, compared to pre-industrial levels. The Paris Agreement of 2015, of which Nigeria is a Party, was a key turning point in the global drive towards the transition to low-emission development.
To achieve this long-term temperature goal, countries aim to reach global peaking of greenhouse gas emissions as soon as possible to achieve a climate-neutral world by mid-century. The Paris Agreement is a landmark in the multilateral climate change process because, for the first time, a binding agreement brings all nations into a common cause to undertake ambitious efforts to combat climate change and adapt to its effects.
What is the Net-Zero Transition?
Net-zero transition means that countries and organizations are cutting greenhouse gas emissions to as close to zero as possible, with any remaining emissions re-absorbed from the atmosphere, by oceans and forests.
The United Nations has stated that there is a growing coalition of countries, cities, businesses, and other institutions pledging to get to net-zero emissions. More than 70 countries, including the biggest polluters – China, the United States, and the European Union – have set a net-zero target, covering about 76% of global emissions.
Over 1000 companies have put in place science-based targets in line with net-zero, and more than 1000 cities, over 1000 educational institutions, and over 400 financial institutions have joined the race to zero, pledging to take rigorous, immediate action to halve global emissions by 2030.
What are the Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies used to solve the problem of Climate Change?
Responding to climate change involves two possible approaches: reducing and stabilizing the levels of heat-trapping greenhouse gases in the atmosphere which is called mitigation and/or adapting to the climate change already in the pipeline which is adaptation.
For mitigation, governments and companies can reduce the burning of fossil fuels used for electricity, heat, and transport. Carbon sinks like the oceans, forests, and soils must be protected to absorb the excess carbon in the atmosphere.
For adaptation, governments can build flood defenses against flooding, especially in coastal communities, have a plan for heatwaves and higher temperatures, and improve water storage and use.
As individuals, we can plant trees, eliminate food waste, reduce meat consumption, use public transport or ride bicycles to work, consume sustainably by buying fewer products, recycle plastics and other recyclable items, use LED Lighting which uses 90% less energy. We collectively need to come together to contribute our own quota to fighting climate change.
-
-
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.
